What Is Trochanteric Bursitis?
Since the 1960s, glucocorticoid infiltration has been the treatment of first choice for trochanteric bursitis.
Trochanteric bursitis is inflammation or irritation of the bursae in the lateral hip bone. This is why this disease is also known as bursitis. The bursa is a fluid-filled sac that acts as a cushion between the muscles, tendons, bones, and joints.
There are two large hip pockets in our body that can typically suffer from irritation or inflammation:
- A pocket covers the bony bulge of the hip bone, the so-called greater trochanter. The inflammation of this pocket is known as trochanteric bursitis.
- Another pocket, that of the psoas illiac, is located in the inner area of the hip. If this pocket becomes infected, it is also called hip bursitis. However, the pain usually occurs in the groin area. This condition isn’t as common but is treated similarly.
Risk factors and causes
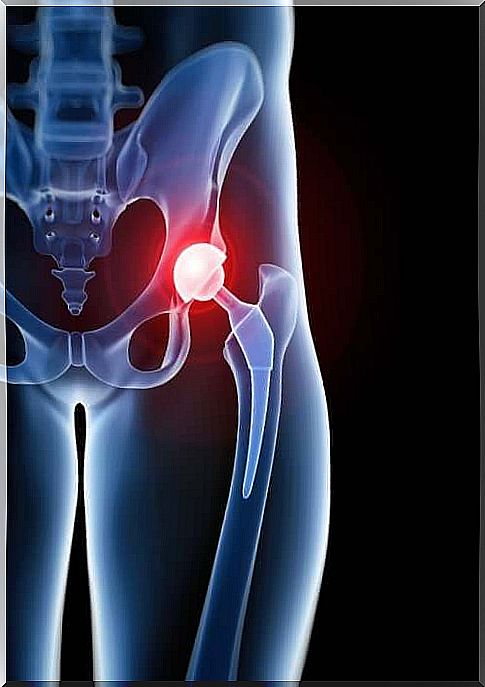
Anyone can have trochanteric bursitis . However, this disease is more common in middle-aged women and men, as well as in the elderly.
There are a number of risk factors that make this hip injury more likely to occur. These include:
- Repetitive Overuse or Overuse Injuries : This type of injury can occur while running, climbing stairs, or doing other activities that require repetitive motion.
- Hip injuries: If the hip is overloaded, there is a risk of injury. Even if you lie on one side for a long time or receive a blow, for example.
- Spinal disorders: such as sclerosis, arthritis, or other problems affecting the spine.
- Differences in the length of the legs: Many people have a longer leg and a shorter leg. This impairment affects the hip bursa throughout.
- Surgery: Hip surgery or prosthetic implants on this joint can irritate the area and cause trochanteric bursitis.
- Bone spurs or calcium deposits: These conditions can develop in the tendons that attach the muscles to the trunk. They can attack the pockets and cause inflammation.
Symptoms of trochanteric bursitis
It is characteristic of trochanteric bursitis that the pain occurs on the side of the hip in the area of the main trunk. This pain can even extend up the upper part of the leg until it reaches the knee and follows the course of the iliotibial ligament.
These symptoms can be more intense when the patient lies down or sits on the affected side. Likewise when he crosses the affected leg over the other, when climbing stairs, or after training or after long periods of sitting or lying down.
Diagnosis of trochanteric bursitis
To diagnose bursitis , the doctor will do a full physical exam. He tries to find the pain by palpating the affected area.
In addition, the patient may need to perform, to rule out other possible injuries or complications other tests. These tests include, among others:
- X-ray: this procedure is usually unspecific. Microcalcifications on the trunk or irregularities in the contour of the main trunk are found in 40% of patients. These do not seem to have any clinical significance. However, the X-ray procedure is useful to rule out coxopathy or infectious truncanteritis.
- Bone tomography : This procedure enables changes in the bone and parilesional calcium deposits to be objectified.
- Magnetic resonance: An MRI shows a non-specific, high-intensity signal in the area of the main stem.
- Scintigraphy
- Ultrasound techniques
Treatment of trochanteric bursitis

Glucocorticoid infiltration has been the treatment of first choice for trochanteric bursitis since the 1960s .
Nevertheless , in the following we will explain in more detail various options for treatment according to their methodology. With this in mind, there are non-invasive and surgical types of treatment.
Non-invasive treatment
Many patients feel relief when they change their lifestyle. For example:
- Avoiding activities that make symptoms worse.
- Take medicines like ibuprofen to relieve inflammation and pain.
- Use tools such as a walking stick.
In addition , physical therapy can be extremely helpful. This strengthens the hips and creates a certain amount of flexibility.
As mentioned earlier, injecting steroids is still the most effective treatment. However, it is important to limit the number of injections so as not to damage the surrounding tissue.
Surgical treatment
This type of treatment is reserved for the most severe cases of trochanteric bursitis. If the bursa remains inflamed and the pain persists after all of the above treatments, your doctor may recommend surgery.
The technique that has been widely used recently is arthroscopic removal of the pouch. In this method , the bursa is removed with an arthroscope or a small camera through a small incision in the hip.